4.Introduction to Nash Equilibrium
Nash Equilibrium is a foundational concept in game theory that describes a situation where players in a game choose their optimal strategies, taking into account the strategies of other players. This concept is essential for understanding how rational agents interact in competitive and cooperative environments. Let’s dive deep into its definition, importance, methods of identification, and several illustrative examples.
Definition and Concept
Nash Equilibrium
A Nash Equilibrium occurs when each player's strategy is optimal, given the strategies of all other players. This means that no player has anything to gain by changing only their strategy unilaterally. In simpler terms, if all players are making the best decision they can, considering the choices of the others, they are in a state of Nash Equilibrium.
Simple Explanation
Consider a scenario where two friends decide where to eat. If one prefers Italian and the other prefers Chinese, they both choose a restaurant based on what they believe the other will pick. If they end up at a restaurant where neither wants to change their choice after seeing the other’s decision, they are in a Nash Equilibrium. Each friend's decision is the best response to the other's choice.
Importance and Implications of Nash Equilibrium
Predictive Power:
Nash Equilibrium provides a framework for predicting the outcomes of strategic interactions. By identifying equilibria, one can anticipate how players will behave in competitive situations.
Stability:
Once players reach a Nash Equilibrium, there is no incentive for any player to deviate from their chosen strategy. This stability is crucial in economic and social systems, as it often leads to predictable and stable outcomes.
Applications Across Fields:
Economics: Businesses can model competitive behaviors, predicting how rivals will react to pricing or product strategies.
Political Science: Voters may choose candidates based on expected voter behavior, leading to strategic campaigning.
Biology: In evolutionary biology, species may adopt survival strategies based on the behaviors of other species, which can be understood through the lens of Nash Equilibrium.
Understanding Rational Behavior:
Analyzing Nash Equilibria helps us understand how rational individuals make decisions in complex environments. This understanding can be applied to various domains, from negotiations to auctions.
Finding Nash Equilibrium
Identifying Nash Equilibria can be accomplished through several methods. One of the most effective is best response analysis.
Best Response Analysis
To find a Nash Equilibrium:
Identify the strategies available to each player.
Determine the payoffs for each combination of strategies.
For each player, find their best response to the strategies chosen by the other players.
Worked Examples
Example 1: Matching Pennies
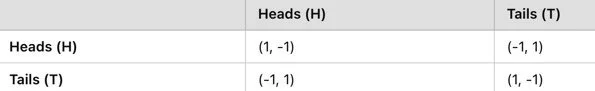
Scenario: Two players, Player A and Player B, simultaneously choose either Heads (H) or Tails (T). Player A wins if both players choose the same side; Player B wins if they choose differently.
Payoff Matrix:
Analysis:
If both choose Heads, Player A gets 1 and Player B gets -1 (A wins).
If both choose Tails, Player A gets -1 and Player B gets 1 (B wins).
If they choose differently, both receive -1.
Finding the Nash Equilibrium:
Player A’s Best Responses:
If Player B plays H, Player A’s best response is H (1 > -1).
If Player B plays T, Player A’s best response is T (-1 > 1).
Player B’s Best Responses:
If Player A plays H, Player B’s best response is T (1 > -1).
If Player A plays T, Player B’s best response is H (-1 > 1).
Conclusion: There is no pure strategy Nash Equilibrium because each player benefits from randomizing their choices. The mixed strategy Nash Equilibrium involves both players choosing Heads or Tails with equal probability (50%). This approach makes them unpredictable, leading to a stable outcome.
Example 2: Coordination Game
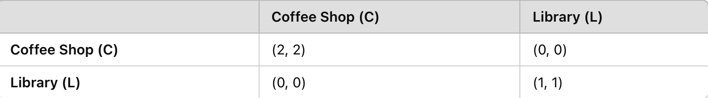
Scenario: Two players, Player A and Player B, need to coordinate their choices between two activities: meeting at a coffee shop (C) or a library (L). Both players prefer to meet at the same place.
Payoff Matrix:
Analysis:
If both meet at the coffee shop, they each get 2 points (2, 2).
If both choose the library, they get 1 point each (1, 1).
If they go to different places, they receive 0 points.
Finding the Nash Equilibrium:
Player A’s Best Responses:
If Player B chooses C, Player A’s best response is C (2 > 0).
If Player B chooses L, Player A’s best response is L (1 > 0).
Player B’s Best Responses:
If Player A chooses C, Player B’s best response is C (2 > 0).
If Player A chooses L, Player B’s best response is L (1 > 0).
Conclusion: The Nash Equilibria in this game are (C, C) and (L, L). Both players can achieve higher payoffs by coordinating their choices, and neither player has an incentive to deviate from these strategies once they are chosen.
Conclusion
Nash Equilibrium serves as a critical tool in game theory, allowing us to analyze strategic interactions and predict outcomes in competitive environments. By utilizing methods like best response analysis, we can identify stable strategies that rational players will adopt.
Questions for Reflection
Why is it significant that Nash Equilibrium does not require players to achieve the best overall outcome?
Answer: Nash Equilibrium emphasizes individual strategy optimality, where players make the best decision given others’ actions. This can lead to suboptimal group outcomes, illustrating the tension between individual rationality and collective efficiency.
In the Matching Pennies example, how does the lack of a pure strategy Nash Equilibrium reflect the nature of the game?
Answer: The absence of a pure strategy Nash Equilibrium indicates that both players must remain unpredictable, relying on mixed strategies to avoid being exploited by the opponent, highlighting the competitive nature of the game.
What are some real-world scenarios where you might see Nash Equilibrium at play?
Answer: Common examples include pricing strategies among competing firms, where each firm's pricing decisions depend on the expected responses of others, or in political campaigns, where candidates adjust their strategies based on their opponents’ actions.
How does understanding Nash Equilibrium help in strategic decision-making in business?
Answer: Businesses can anticipate competitor responses to their strategies, allowing them to devise more effective pricing, marketing, and product development strategies. This foresight can lead to a more stable market position and better overall outcomes.